👩🏫 Architecture and cloud setup (Work In Progress)
This section describes a cloud architecture on how oss version of nocodb is hosted on cloud for saas offering (nocohub.ai), including information about the security, deployment, operations and operations playbooks.
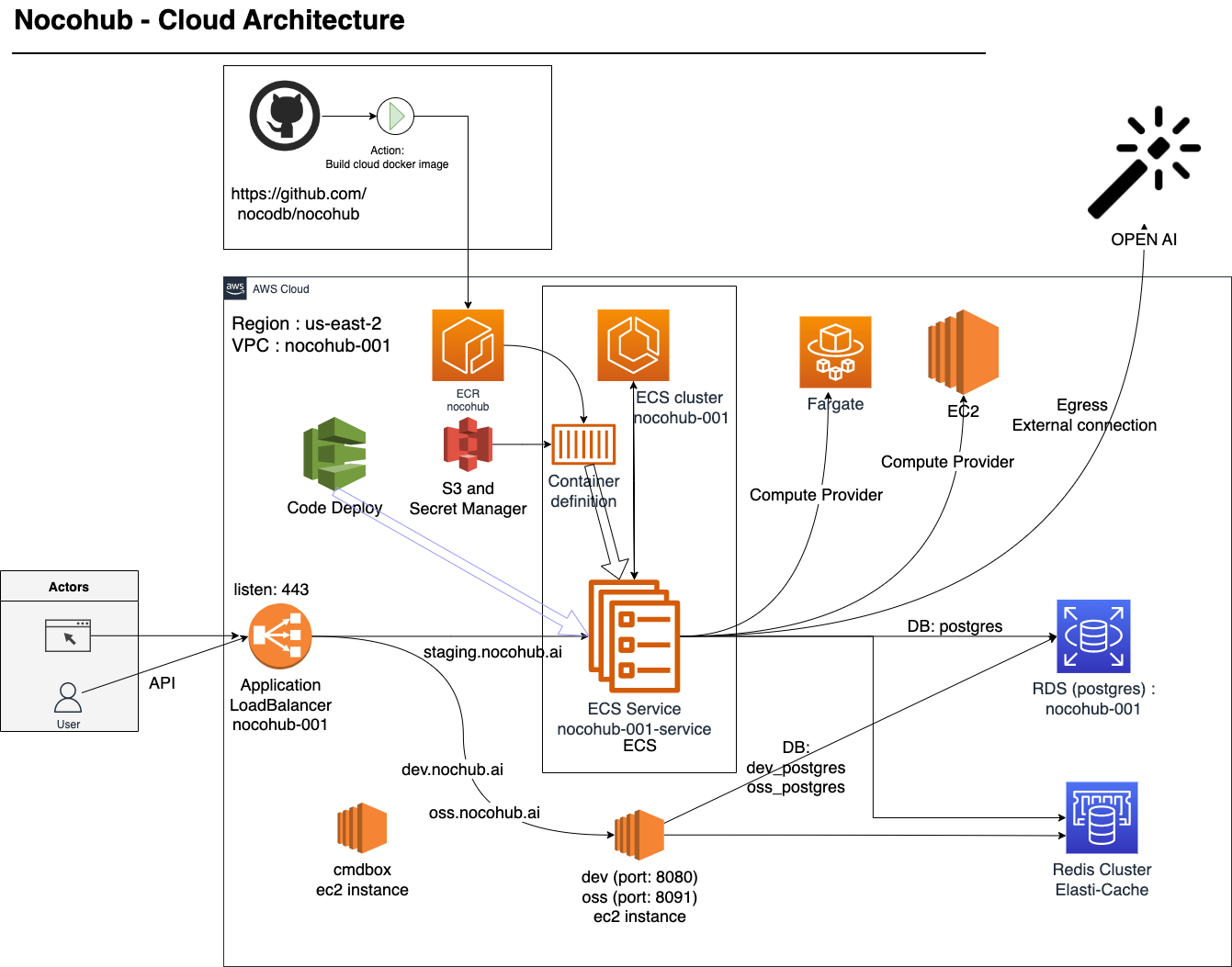
Architecture:
Architecture Diagram
Core Components
- nocohub (an extension to nocodb with added enterprise features)
- redis (for metadata cache)
- postgres (database)
AWS components for hosting / Cloud Setup:
we have chosen AWS as cloud provider and leverage many of the aws services in hosting saas offering. Below are some of the important services being used but not limited
-
ECS for scalabilty: Amazon ECS is a fully managed container orchestration service that makes it easy for you to deploy, manage, and scale containerized applications.
- Fargate and EC2 for instances
- Autoscaling : asg and launch configurations
- Network and Security : security groups
-
ECR
-
S3
-
Cloud watch for monitoring dashboards
-
Network : VPC for network isolation, AWS Application Loadbalancers and target groups for traffic control
Security:
- AccessControl : leverage AWS VPCs and security groups to isolate access to instances and datastores.
- Encryption : Secret Manager for persisting secure information and network traffic via SSL (certs created via SSL Manager)
Monitoring and Management: CloudWatch : Leverage cloud watch for monitoring our systems and below is the dashboard. nocohub master dashboard can be used to observe the metrics of lb, ecs, redis and rds
Deployment and Operations
Deployment : Deployment refers to rollout of nocohub application which is hosted in ECS and requires a new docker image to be rolled out. It is expected that docker image tag RC_M.m.p is availabe in container registry.
Proposed Approach for deployment
- Register new ECS Task Definition with image url pointing to RC_M.m.p
- Invoke AWS Code Deploy with new task definition.
- Code deploy performs the canary rollout (rollback if test fails)
TODO:
- include rollout scripts and create trigger point an api or github action for the same
- canary tests to be implemented and rollback if tests fail
- Rollout alerts to slack channel
- Rollback troubleshooting documentation
- Proposal for db schema changes
As a temporary solution, There is check if there is new image available as latest tag in ECR and when found, aws code deploy. This script is running in EC2 instance here
Operations :
- Alerts to be configured.
- including performance metrics,
- logging, and incident response.
Cost Analysis:
| AWS Service | Type / Size | Cost | Note | Currently Preffered |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EC2 | t3.small 2vCPU/2gb | $0.0208 USD per Hour | Two containers in one instance | Yes |
| t3.micro 2vCPU/1GB | $0.0104 per Hour | Only one container can be run | No | |
| EBS | 8GB per EC2 instance | $0.1 per GB/month | Can be reduced to smaller size | |
| Fargate | 2vCPU/2GB | $5 per month per instance | Refer example 4 on here , Issues with customizing VPCs. PG wont be accessible if made private | Yes |
| RDS | db.t3.medium (2vCPU / 4GB) | $60 per month additional storage and backups will cost more | Production will require bigger cpu/memory | Yes |
| LB | Application Loadbalancer | $40 - $50 with light traffic | traffic/network IO, and logging will increase the cost | Yes |
| Elasti-Cache | cache.t4g.small * 3 instances | $70-$90 | TODO: too expensive for the usage, reduce the size here | MayBe |
| ECR/S3 | Minor |
Tools comparision:
TODO : make a table structure and add more details eks vs ecs vs app runner
Conclusion and Future Work:
- Kubernetes / EKS : Kubernetes setup comes up with additional maintainance overhead but this would be ideal to maintain same setup for saas and support on-premise setup customised for customers choice of cloud. our cloud setup and customer. Since on-prem/multi cloud is out of scope at the moment.
- Better support for multi-single-tenant and multi-tenant to support special isolation requirements from customers (support one click setup). This would also require application level changes
- database split read and write paths
- Explore cost effective options like
- fargate with ECS
- spot instances for autoscaling